
A British scientific expedition has discovered the world’s deepest undersea volcanic vents, known as ‘black smokers’, 3.1 miles (5,000 metres) down in the Cayman Trough in the Caribbean.
Using a deep-diving vehicle remotely controlled from the Royal Research Ship James Cook, the scientists found slender spires made of copper and iron ores on the…

The 3rd International Ocean Stewardship Forum (IOSF), a conference designed to promote greater integration between the legal and technical aspects of marine policy-making has been cancelled.
https://www.oceanstewardship.com
The aim of the forum is bringing together leading marine scientists, policy-makers and…
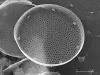
The movement of ocean eddies and other surface water masses over short timescales causes rapid changes in the community composition of marine algae (phytoplankton) in the sunlit upper ocean, according to new findings.
The research, which was conducted by scientists of the National Oceanography Centre (NOC), spotlights intimate links between surface…

Some regions of the deep ocean floor support abundant populations of organisms, despite being overlain by water that contains very little oxygen, according to an international study led by scientists at the National Oceanography Centre, Southampton. But global warming is likely to exacerbate oxygen depletion and thereby reduce biodiversity in these…

Spore-like reproductive cysts of enigmatic organisms called acantharians rapidly sink from surface waters to the deep ocean in certain regions, according to new research.
Scientists suspect that this is part of an extraordinary reproductive strategy, which allows juveniles to exploit a seasonal food bonanza.
The research shows that deep…

Scientists have discovered that, in moderate conditions, the release of dimethyl sulphide (DMS), from the ocean surface increases linearly with wind speed
The exchange of gases between the oceans and the atmosphere has an important influence on climate. Scientists have discovered that, in moderate conditions, the release of one such gas, dimethyl…

The impact on levels of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere by the decaying remains of a group of marine creatures that includes starfish and sea urchin has been significantly underestimated, conclude scientists.
“Climate models must take this carbon sink into account,” says Mario Lebrato, lead author of the study. The work was done when he…