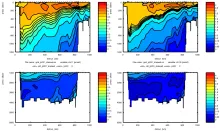
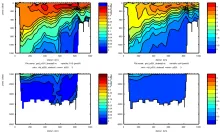
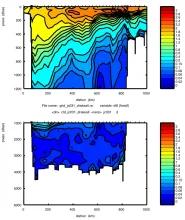
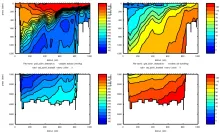
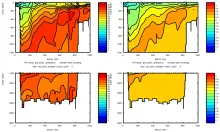
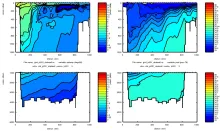
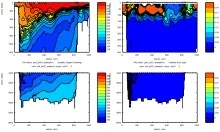
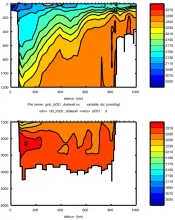
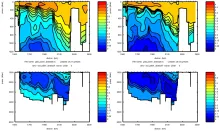
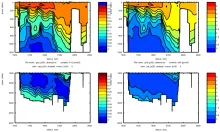
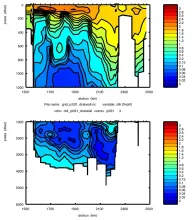
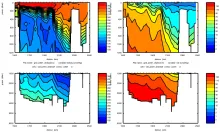
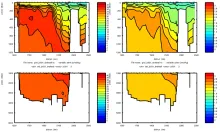
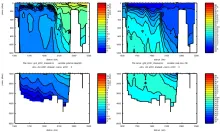
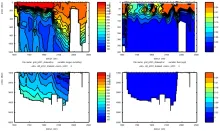
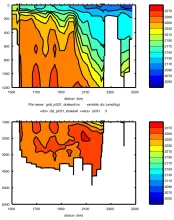
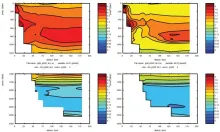
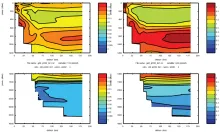
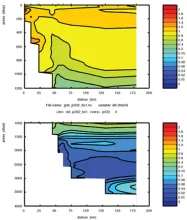
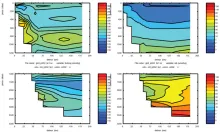
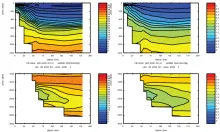
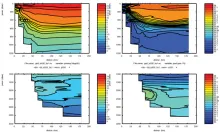
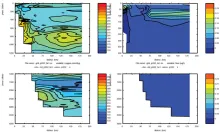
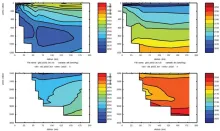
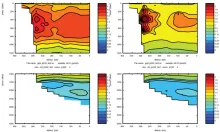
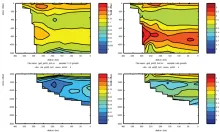
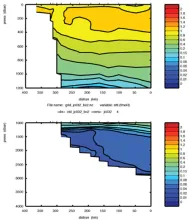
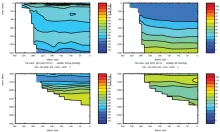
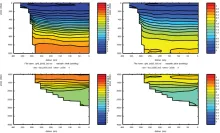
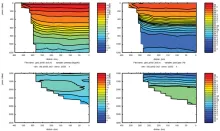
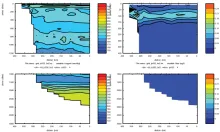
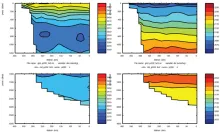
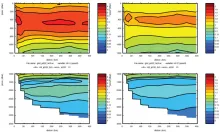
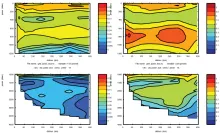
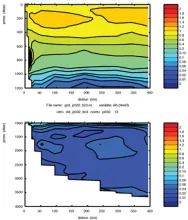
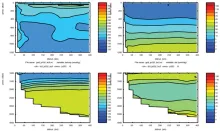
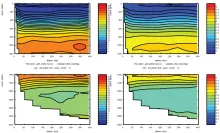
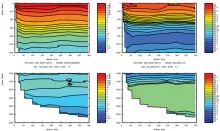
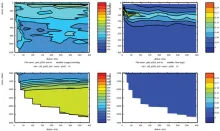
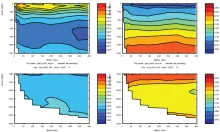
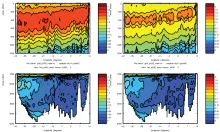
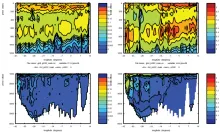
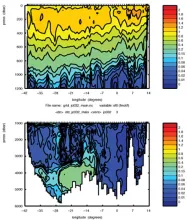
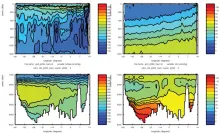
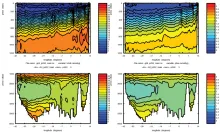
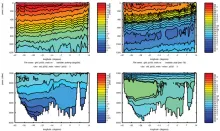
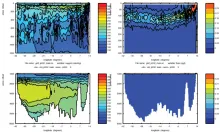
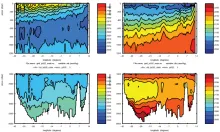
To monitor changes and improve understanding of the dynamics of the Southern Ocean by continuing a long time series of repeat hydrographic measurements across the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) in Drake Passage.
Cruises and Data
Each cruise is relatively short, typically around three weeks at sea rather than the six weeks more commonly required for a major hydrographic expedition. The SR1b section has often been combined with other work in the area, as well as with logistics for research stations along the Antarctic Peninsula. Recent cruises are featured on our cruise blog.
In addition to establishing a unique time series of ocean measurements leading to interesting science results, the cruises have fostered collaboration between NERC institutes and Higher Education Institute groups, have provided many PhD students with an opportunity to experience deep-ocean physical oceanography fieldwork, and have been used to test and develop new measurement techniques.
Completed cruises
| Season | Start Date* | End Date* | Cruise Code | Outputs | Baroclinic Transport (Sv)** | Transport-Weighted Potential Temperature (°C)*** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993/94 | 21/11/1993 | 26/11/1993 | JR0a/JR00_1 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 134 | 2.22 |
| 1994/95 | 15/11/1994 | 21/11/1994 | JR0b/JR00_2 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 141 | 2.14 |
| 1995/96 | no cruise | |||||
| 1996/97 | 15/11/1996 | 20/11/1996 | JR16 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 125 | 2.18 |
| 1997/98 | 29/12/1997 | 07/01/1998 | JR27 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 146 | 2.21 |
| 1998/99 | no cruise | |||||
| 1999/00 | 12/02/2000 | 17/02/2000 | JR47 | Report | BODC | 143 | 2.33 |
| 2000/01 | 22/11/2000 | 28/11/2000 | JR55 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 142 | 2.22 |
| 2001/02 | 20/11/2001 | 26/11/2001 | JR67 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 132 | 2.14 |
| 2002/03 | 27/12/2002 | 01/01/2003 | JR81 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 134 | 2.04 |
| 2003/04 | 11/12/2003 | 15/12/2003 | JR94 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 145 | 2.26 |
| 2004/05 | 02/12/2004 | 08/12/2004 | JR115 | Report | BODC | 127 | 2.07 |
| 2005/06 | 07/12/2005 | 12/12/2005 | JR139 | Report | BODC | 133 | 2.23 |
| 2006/07 | 08/12/2006 | 12/12/2006 | JR163 | Report | BODC | 127 | 2.20 |
| 2007/08 | 30/11/2007 | 05/12/2007 | JR193 | Report | BODC | 135 | 2.16 |
| 2008/09 | 13/12/2008 | 18/12/2008 | JR194 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 131 | 2.29 |
| 2008/09 | 20/02/2009 | 26/02/2009 | JC031 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 133 | 2.33 |
| 2009/10 | 19/11/2009 | 26/11/2009 | JR195 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 115 | 2.01 |
| 2010/11 | 01/12/2010 | 17/12/2010 | JR242 | | BODC | incomplete | |
| 2010/11 | 21/04/2011 | 25/04/2011 | JR276 | Report | BODC | incomplete | |
| 2011/12 | 28/11/2011 | 05/12/2011 | JR265 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 132 | 2.14 |
| 2011/12 | 07/03/2012 | 11/03/2012 | JC069 | Report | BODC | incomplete | |
| 2012/13 | 18/03/2013 | 27/03/2013 | JR281 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 134 | 2.03 |
| 2013/14 | 12/03/2014 | 02/04/2014 | JR299 | Report | BODC (I), (II) | 147 (discontinuous) | 2.12 |
| 2014/15 | 13/01/2015 | 18/01/2015 | JR306 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 159 | 2.20 |
| 2015/16 | 06/01/2016 | 12/01/2016 | JR15003 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 121 | 2.05 |
| 2016/17 | 08/11/2016 | 05/12/2016 | JR16002 | Report | BODC | Hydro | 130 | 2.28 |
| 2017/18 | 15/12/2017 | 18/12/2017 | JR17001 | Report | BODC | 130 (missing northern slope) | 2.48 |
| 2018/19 | 03/11/2018 | 21/11/2018 | JR18002 | Report | BODC | 135 | 2.16 |
| 2019/20 | 03/02/2020 | 13/03/2020 | DY113 |
*start and end date of measurements
**relative to deepest common level (reference level varies from occupation to occupation); 1 Sv = 1 million cubic metres per second
***transport-weighted mean potential temperature seasonally adjusted to December
Publications from SR1b include peer-reviewed articles and reviews, masters and doctoral theses, cruise reports, and other articles and reports. If you have used SR1b data and your publication is not listed here, please contact us.
Journal Research Articles
Abrahamsen, E. P., Meijers, A. J. S., Polzin, K., Naveira Garabato, A. C., King, B. A., Firing, Y. L., Sallée, J.-B., Sheen, K., Gordon, A., Huber, B., Meredith, M., (2019) Stabilisation of dense Antarctic water supply to the Atlantic Ocean overturning circulation, Nat. Clim. Chang., doi: 10.1038/s41558-019-0561-2.
Firing, Y. L., E. L. McDonagh, B. A. King, and D. G. Desbruyères, (2017) Deep temperature variability in Drake Passage, J. Geophys. Res., 122 (1), 713-725, doi: 10.1002/2016jc012452.
Meijers, A. J. S., M. P. Meredith, E. P. Abrahamsen, M. A. Morales Maqueda, D. Jones, and A. C. Naveira Garabato, (2016) Wind-driven export of Weddell Sea slope water, J. Geophys. Res., 121 (10), 7530-7546, doi:10.1002/2016jc011757.
Naveira Garabato, A. C., K. L. Polzin, R. Ferrari, J. D. Zika, and A. Forryan, (2016) A microscale view of mixing and overturning across the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 46, 233-254, doi:10.1175/jpo-d-15-0025.1.
Talley, L., et al., (2016) Changes in ocean heat, carbon content, and ventilation: a review of the first decade of GO-SHIP global repeat hydrography, Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci., 8, 185–215, doi:10.1146/annurev-marine-052915-100829.
Chidichimo, M. P., K. A. Donohue, D. R. Watts, and K. L. Tracey, (2014) Baroclinic transport time series of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current measured in Drake Passage, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 44, 1829-1853, doi:10.1175/jpo-d-13-071.1.
Evans, D. G., J. D. Zika, A. C. N. Garabato, and A. J. G. Nurser, (2014) The imprint of Southern Ocean overturning on seasonal water mass variability in Drake Passage, J. Geophys. Res., 119, 7987–8010, doi:10.1002/2014jc010097.
Meredith, M. P., L. Jullion, P. J. Brown, A. C. Naveira Garabato, and M. P. Couldrey, (2014) Dense waters of the Weddell and Scotia Seas: recent changes in properties and circulation, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A, 372, doi:10.1098/rsta.2013.0041.
Sheen, K. L., A. C. Naveira Garabato, J. A. Brearley, M. P. Meredith, K. L. Polzin, D. A. Smeed, A. Forryan, B. A. King, J.-B. Sallée, L. St. Laurent, A. M. Thurnherr, J. M. Toole, S. N. Waterman, and A. J. Watson, (2014) Eddy-induced variability in Southern Ocean abyssal mixing on climatic timescales, Nat. Geosci., 7, 577–582, doi:10.1038/ngeo2200.
Close, S. E., A. C. Naveira Garabato, E. L. McDonagh, B. A. King, M. Biuw, and L. Boehme, (2013) Control of mode and intermediate water mass properties in Drake Passage by the Amundsen Sea Low, J. Clim., 26 , 5102–5123, doi:10.1175/jcli-d-12-00346.1.
Jullion, L., A. C. Naveira Garabato, M. P. Meredith, P. R. Holland, P. Courtois, and B. A. King, (2013) Decadal freshening of the Antarctic Bottom Water exported from the Weddell Sea, J. Clim., 26 , 8111–8125, doi:10.1175/jcli-d-12-00765.1.
Purkey, S. G., and G. C. Johnson, (2013) Antarctic Bottom Water warming and freshening: contributions to sea level rise, ocean freshwater budgets, and global heat gain, J. Clim., 25, 6105–6122, doi:10.1175/jcli-d-12-00834.1.
Close, S. E., and A. C. Naveira Garabato, (2012) Baroclinic adjustment in Drake Passage driven by tropical Pacific forcing, Geophys. Res. Lett., 39, doi:10.1029/2012gl053402.
Purkey, S. G., and G. C. Johnson, (2012) Global contraction of Antarctic Bottom Water between the 1980s and 2000s, J. Clim., 25, 5830–5844, doi:10.1175/jcli-d-11.00612.1.
Naveira Garabato, A. C., R. Ferrari, and K. L. Polzin, (2011) Eddy stiring in the Southern Ocean, J. Geophys. Res., 116, C09019, doi:10.1029/2010jc006818.
Jullion, L., S. C. Jones, A. C. Naveira Garabato, and M. P. Meredith, (2010) Wind-controlled export of Antarctic Bottom Water from the Weddell Sea, Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, doi:10.1029/2010gl042822.
Naveira Garabato, A. C., L. Jullion, D. P. Stevens, K. J. Heywood, and B. A. King, (2009) Variability of Subantarctic Mode Water and Antarctic Intermediate Water in the Drake Passage during the late-twentieth and early-twenty-first centuries, J. Clim., 22 , 3661–3688, doi:10.1175/2009jcli2621.1.
Cunningham, S., and M. Pavic, (2007) Surface geostrophic currents across the Antarctic Circumpolar Current in Drake Passage from 1992 to 2004, Prog. Oceanogr., 73, 296–310, doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2006.07.010.
Heywood, K. J., J. L. Collins, C. W. Hughes, and I. Vassie, (2007) On the detectability of internal tides in Drake Passage, Deep Sea Res. I, 54, 1972–1984, doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2007.08.002.
Williams, A., S. Bacon, and S. Cunningham, (2006) Variability of the Lower Circumpolar Deep Water in Drake Passage 1926-2004, Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, doi:10.1029/2005gl024226.
Naveira Garabato, A. C., K. L. Polzin, B. A. King, K. J. Heywood, and M. Visbeck, (2004) Widespread intense turbulent mixing in the Southern Ocean, Science, 303, 210–213, doi:10.1126/science.1090929.
Sokolov, S., B. A. King, S. R. Rintoul, and R. L. Rojas, (2004) Upper ocean temperature and the baroclinic transport stream function relationship in Drake Passage, J. Geophys. Res., 109, doi:10.1029/2003jc002010.
Bryden, H. L., and S. A. Cunningham, (2003) How wind-forcing and air-sea heat exchange determine the meridional temperature gradient and stratification for the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, J. Geophys. Res., 108, 3275, doi:10.1029/2001jc001296.
Cunningham, S. A., S. G. Alderson, B. A. King, and M. A. Brandon, (2003) Transport and variability of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current in Drake Passage, J. Geophys. Res., 108, 8084, doi:10.1029/2001jc001147.
Meredith, M. P., C. W. Hughes, and P. R. Foden, (2003) Downslope convection north of Elephant Island, Antarctica: Influence on deep waters and dependence on ENSO, Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, doi:10.1029/2003gl017074.
Naveira Garabato, A. C., D. P. Stevens, and K. J. Heywood, (2003) Water mass conversion, fluxes, and mixing in the Scotia Sea diagnosed by an inverse model, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 33, 2565–2587, doi:10.1175/1520-0485(2003)033<2565:WMCFAM>2.0.CO;2.
Rubython, K. E., K. J. Heywood, and J. M. Vassie, (2001) Interannual variability of bottom temperatures in Drake Passage, J. Geophys. Res., 106, 2779–2793, doi:10.1029/2000JC900114.
Sanders, R., and T. Jickells, (2000) Total organic nutrients in Drake Passage, Deep Sea Res. I, 47, 997–1014, doi:10.1016/s0967-0637(99)00079-5.
Alderson, S. G., and S. A. Cunningham, (1999) Velocity errors in Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler measurements due to platform attitude variations and their effect on volume transport estimates, J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech., 16, 96–106, doi:10.1175/1520-0426(1999)016<0096:VEIZDC>2.0.CO;2.
Arhan, M., K. J. Heywood, and B. A. King, (1999) The deep waters from the Southern Ocean at the entry to the Argentine Basin, Deep Sea Res. II , 46 , 475–499, 10.1016/s0967-0645(98)00110-6.
Meredith, M. P., K. E. Grose, E. L. McDonagh, K. J. Heywood, R. D. Frew, and P. F. Dennis, (1999) Distribution of oxygen isotopes in the water masses of Drake Passage and the South Atlantic, J. Geophys. Res., 104, 20949–20962, doi:10.1029/98jc02544.
Meredith, M. P., J. M. Vassie, R. Spencer, and K. J. Heywood, (1997) The processing and application of inverted echo sounder data from Drake Passage, J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech., 14, 871–882, doi:10.1175/1520-0426(1997)014<0871:TPAAOI>2.0.CO;2.
King, B. A., S. G. Alderson, and D. Cromwell, (1996) Enhancement of shipboard ADCP data with DGPS position and GPS heading measurements, Deep Sea Res. I, 43, 937–947, doi:10.1016/0967-0637(96)00033-7.
Meredith, M. P., J. M. Vassie, K. J. Heywood, and R. Spencer, (1996) On the temporal variability of the transport through Drake Passage, J. Geophys. Res., 101, 22485–22494, doi:10.1029/96JC02003.
Reviews
Meredith, M. P., et al., (2011) Sustained monitoring of the Southern Ocean at Drake Passage: past achievements and future priorities, Rev. Geophys., 49, doi:10.1029/2010rg000348.
Rintoul, S. R., J. Church, E. Fahrbach, M. Garcia, A. Gordon, B. King, R. Morrow, A. H. Orsi, and K. Speer, (2001) Monitoring and understanding Southern Ocean variability and its impact on climate: a strategy for sustained observations, in Observing the ocean for climate in the 21st century, edited by C. Koblinsky and N. Smith, pp. section 5.4, 486–510, GODAE Project Office, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Australia, 2001.
Theses
Dibb, M. K., (2019) Assessing if the Antarctic Circumpolar Current transport in Drake Passage is changing over time, University of Southampton MSci Thesis.
Dragomir, O. C., (2017) Reconciling definitions of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current fronts in Drake Passage, University of Southampton MSc Thesis, 55 pp.
Evans, D. G., (2016) Heating and cooling or ebbing and flowing? Oceanic change from a thermocline perspective, University of Southampton Doctoral Thesis, 131 pp.
Evans, G. R. (2013) A study of the South Atlantic Ocean: Circulation and carbon variability, University of Southampton Doctoral Thesis, 343 pp.
Jullion, L., (2008) Water mass modification in the South Western Atlantic, University of East Anglia Doctoral Thesis, 243 pp.
Williams, A. P., (2008) Antarctic climate: Oceanic fluxes and variability, University of Southampton Doctoral Thesis, 204 pp.
Price, M. R., (2005) Processes governing interannual variability in Drake Passage, PhD Thesis.
Corbel, G., (2003) Spatio-temporal circulation variability in the vicinity of Drake Passage in OCCAM, University of Southampton MSc Thesis, 72 pp.
Marwood, T. J., (2000) Antarctic Intermediate Water and the Antarctic Circumpolar Current in the Southwest Atlantic, University of East Anglia PhD Thesis.
Rubython, K. E., (2000) Ocean variability in the Drake Passage and Scotia Sea region of the Southern Ocean, University of East Anglia PhD Thesis.
Cruise Reports
Firing, Y.L. (ed.) (2019) Repeat hydrographic measurements on GO-SHIP line SR1b. Southampton, UK, National Oceanography Centre, 90pp. (National Oceanography Centre Cruise Report No. 58)
Barnes, D.K.A., Brearley A., Firing, Y., Scourse J., and 25 others (2018) Scientific cruise report JR17001 RRS James Clark Ross NERC ICEBERGS & ORCHESTRA projects 2017. Cambridge, UK, British Antarctic Survey, 175pp.
Firing, Y. (ed.) (2017) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise JR16002, 10 Nov - 03 Dec 2016, Hydrographic measurements on GO-SHIP line SR1b. Southampton, UK, National Oceanography Centre Southampton, 43pp. (National Oceanography Centre Cruise Report No. 41)
Firing, Y. (ed.) (2016) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise JR15003, 17 Dec 2015 - 13 Jan 2016. Hydrographic measurements on GO-SHIP line SR1b and investigations of circulation and isotope cycles in coastal West Antarctica. Southampton, UK, National Oceanography Centre Southampton, 41pp. (National Oceanography Centre Cruise Report No. 38)
King, B.A. and Y. Firing (2015) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise JR306, 10 - 20 Jan 2015. Hydrographic measurements on WOCE line SR1b. Southampton, UK, National Oceanography Centre Southampton, 35pp. (National Oceanography Centre Cruise Report No. 31)
Meijers, A. (ed.) (2014) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise JR299, 8 Mar - 19 Apr 2014. Scotia Sea circumnavigation and DIMES UK5. Cambridge, UK, British Antarctic Survey, 176pp.
Sallée, J.-B. (ed.) (2013) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise JR281, 14 Mar - 26 Apr 2013. JR273A - JR272B - JR252B - JR278, UKD-4. Cambridge, UK, British Antarctic Survey, 150pp.
Naveira Garabato, A.C. and A. Watson (eds.) (2012) RRS James Cook Cruise JC069, 31 Jan - 22 Mar 2012. DIMES UK 3. Southampton, UK, University of Southampton, 137pp.
Yelland, M.J. (2011) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise JR265, 27 Nov - 24 Dec 2011. Part I: The Drake Passage hydrographic repeat section SR1b. Southampton, UK, National Oceanography Centre Southampton, 135pp. (National Oceanography Centre Cruise Report No. 10)
Watson, A. (ed.) (2011) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise JR276, 9 - 26 Apr 2011. DIMES UK 2.5. Norwich, UK, University of East Anglia, 115pp.
Yelland, M.J. (2009) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise 195, 18-29 Nov 2009. Drake Passage repeat hydrography of WOCE section SR1b: a beginners guide. Southampton, UK, National Oceanography Centre Southampton, 123pp. (National Oceanography Centre Southampton Cruise Report, 45)
McDonagh, E.L., Hamersley, D.R.C. and McDonagh, E.L. (eds.) (2009) RRS James Cook Cruise JC031, 03 Feb-03 Mar 2009. Hydrographic sections of Drake Passage. Southampton, UK, National Oceanography Centre Southampton, 170pp. (National Oceanography Centre Southampton Cruise Report, 39)
Stansfield, K. and Meredith, M. (2008) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise 139, 05 Dec-12 Dec 2005. Drake Passage Repeat Hydrography: WOCE Southern Repeat Section 1b Burdwood Bank to Elephant Island. Southampton, UK, National Oceanography Centre Southampton, 72pp. (National Oceanography Centre Southampton Cruise Report, 24)
Williams, A.P. and Hadfield, R.E. Quartly, G.D. (ed.) (2008) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise 163, 07 Dec-15 Dec 2006. Drake Passage Repeat Hydrography: WOCE Southern Repeat Section 1b - Burdwood Bank to Elephant Island. Southampton, UK, National Oceanography Centre Southampton, 64pp. (National Oceanography Centre Southampton Cruise Report, 25)
Bacon, S. and Cunningham, S.A. (eds.) (2005) Drake Passage summary report: Cruises on RRS "James Clark Ross", 1993-2000. Drake Passage repeat hydrography: WOCE Southern Repeat Section 1b - Elephant Island to Burdwood Bank. Southampton, UK, Southampton Oceanography Centre, 151pp. (Southampton Oceanography Centre Cruise Report, 44)
Hawker, E.J., King, B.A. and Sparrow, M. (2005) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise 94, 01 Dec-15 Dec 2003. Drake Passage repeat hydrography: WOCE Southern Repeat Section 1b - Burdwood Bank to Elephant Island. Southampton, UK, Southampton Oceanography Centre, 56pp. (Southampton Oceanography Centre Cruise Report, 55)
Sparrow, M. and Hawker, E.J. (2005) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise 115, 01 Dec-19 Dec 2004. Drake Passage repeat hydrography: WOCE Southern Repeat Section 1b - Burdwood Bank to Elephant Island. Southampton, UK, Southampton Oceanography Centre, 80pp. (Southampton Oceanography Centre Cruise Report, 56)
Bacon, S (2003) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise 81, 18 Dec 2002-02 Jan 2003. Drake Passage repeat hydrography: WOCE Southern Repeat Section 1b Elephant Island to Burdwood Bank. Southampton, UK, Southampton Oceanography Centre, 86pp. (Southampton Oceanography Centre Cruise Report, 43)
Bacon, S. (2002) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise 67, 19 Nov-17 Dec 2002. Drake Passage repeat hydrography: WOCE Southern Repeat Section 1b Burdwood Bank to Elephant Island. Southampton, UK, Southampton Oceanography Centre, 118pp. (Southampton Oceanography Centre Cruise Report, 38)
Cunningham, S.A. (2001) RRS James Clark Ross Cruise JR55, 21 Nov-14 Dec. Drake Passage repeat hydrography: WOCE Southern Section 1b Burdwood Bank to Elephant Island. Southampton, UK, Southampton Oceanography Centre, 75pp. (Southampton Oceanography Centre Cruise Report, 35)
Other
Cattle, H. and Sparrow, M. (eds.) (2005) CLIVAR Exchanges No. 35, Southern Hemisphere climate variability
Cunningham, S.A. (2005) Southern ocean circulation. Archives of Natural History, 32, 265-280.